What Is Data Integration? A Complete Guide for 2026
Introduction
Your sales team uses Salesforce. Your marketing team relies on HubSpot. Your finance department lives in QuickBooks. And your customer data? It’s scattered across all three—plus a dozen other systems.
Sound familiar? This is the reality for most modern businesses. Data silos aren’t just inconvenient—they cost companies millions in lost insights, duplicated efforts, and missed opportunities.
That’s where data integration comes in. It’s the process that connects your fragmented data sources, giving you a unified view of your business operations. Whether you’re a startup founder making your first data hire or an enterprise leader managing complex data ecosystems, understanding what data integration is and how it works is critical to staying competitive in today’s data-driven landscape.
What Is Data Integration?
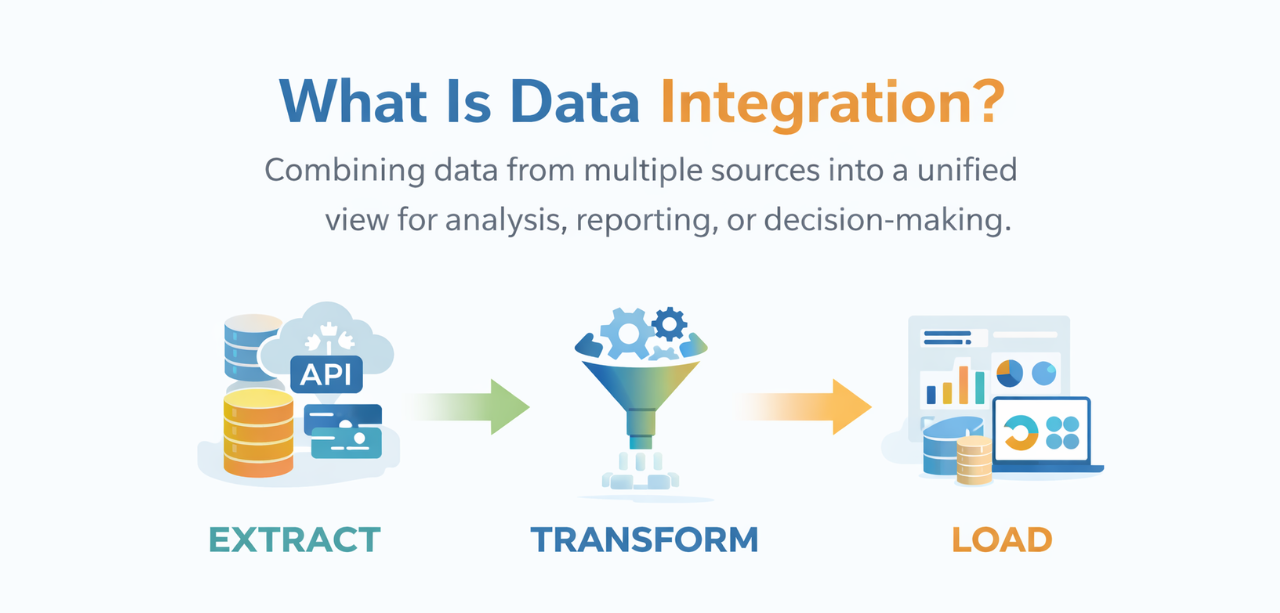
Data integration is the process of combining data from multiple sources into a single, unified view that provides consistent access and delivery of data across an organization. It involves collecting, cleaning, transforming, and consolidating data from disparate systems—such as databases, cloud applications, APIs, and legacy systems—to make it accessible for analysis, reporting, and decision-making.
Rather than manually pulling reports from different systems or working with incomplete datasets, data integration creates automated data pipelines that keep information synchronized and accurate. The result is a centralized data warehouse or data lake where business users can access reliable, up-to-date information without technical barriers.
Think of it as building bridges between isolated islands of data. Each system in your organization generates valuable information, but that value multiplies exponentially when these systems can communicate and share data seamlessly.
Why Is Data Integration Important?
Data integration has evolved from a “nice-to-have” technical project to a business-critical function. Here’s why it matters:
- Business Intelligence and Analytics: Without integrated data, your analytics are only as good as your most limited data source. Integration enables comprehensive reporting that draws insights from your entire data ecosystem.
- Operational Efficiency: Manual data transfer between systems wastes countless hours. Automated data integration eliminates repetitive tasks, reduces human error, and frees your team to focus on strategic work.
- Customer Experience: When your customer service, sales, and marketing teams all work from the same integrated customer data, you deliver more personalized, consistent experiences across every touchpoint.
- Compliance and Governance: Regulatory requirements like GDPR and CCPA demand accurate, traceable data. Integration helps maintain data lineage and ensures compliance across all systems.
- Real-Time Decision Making: Modern business moves fast. Integrated data systems enable real-time dashboards and alerts that help you respond to opportunities and challenges as they happen.
According to industry reports, organizations that implement effective data integration strategies see up to 30% improvement in operational efficiency and significantly faster time-to-insight for business intelligence initiatives.
How Does Data Integration Work?
The data integration process typically follows these key steps:
1. Data Discovery and Mapping First, you identify all relevant data sources—databases, SaaS applications, APIs, flat files, and more. Then you map out which data fields from each source need to be integrated and how they relate to each other.
2. Data Extraction Data is pulled from source systems using connectors, APIs, or database queries. This can happen on a scheduled basis (batch processing) or continuously (real-time streaming).
3. Data Transformation Raw data rarely fits together perfectly. This step involves cleaning, standardizing, and transforming data into a consistent format. You might convert date formats, standardize naming conventions, deduplicate records, or calculate derived values.
4. Data Loading The transformed data is loaded into a target system—typically a data warehouse, data lake, or operational database where it can be accessed by downstream applications and users.
5. Data Quality and Monitoring Ongoing validation ensures data accuracy, completeness, and consistency. Monitoring systems alert teams to any integration failures, data quality issues, or performance problems.
6. Data Delivery Finally, integrated data is made available to end users through business intelligence tools, dashboards, reports, or APIs that feed other applications.
Types of Data Integration
Different business needs require different integration approaches. Here are the most common types:
- ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) The traditional approach where data is extracted from sources, transformed in a staging area, and then loaded into a target system. ETL works well for batch processing and situations where data needs significant transformation before use.
- ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) A modern variation where data is loaded into the target system first, then transformed using the processing power of cloud data warehouses like Snowflake or BigQuery. ELT is faster for large datasets and leverages modern cloud infrastructure.
- Data Virtualization Instead of physically moving data, virtualization creates a virtual layer that provides unified access to data across multiple sources. The data stays in place, but users query it as if it were in one location.
- Real-Time Data Integration Streaming integration captures and processes data continuously as it’s generated. This is essential for use cases like fraud detection, live dashboards, or IoT applications where immediate insights matter.
- API-Based Integration Modern cloud applications communicate through APIs. API integration connects SaaS platforms and cloud services, enabling bidirectional data flow between systems like Salesforce, Slack, and Stripe.
Data Integration vs ETL: What’s the Difference?
Many people use these terms interchangeably, but there’s an important distinction:
| Aspect | Data Integration | ETL |
| Scope | Broad category covering all methods of combining data | Specific method of data integration |
| Approach | Includes ETL, ELT, virtualization, APIs, and more | Extract, Transform, Load process only |
| Timing | Can be real-time, near real-time, or batch | Typically batch processing |
| Flexibility | Encompasses multiple techniques | One specific technique |
| Use Case | General term for any data combination need | Best for structured data warehouse scenarios |
Key Takeaway: ETL is a type of data integration, but data integration includes many approaches beyond ETL. Think of data integration as the goal and ETL as one tool to achieve it.
Real-World Data Integration Examples
- E-Commerce Retail An online retailer integrates data from their Shopify store, inventory management system, Stripe payment processor, and email marketing platform. This gives them real-time visibility into sales, inventory levels, customer behavior, and marketing ROI—all in one dashboard.
- Healthcare Provider A hospital system integrates electronic health records, billing systems, insurance verification, and lab results. Doctors access complete patient histories instantly, reducing errors and improving care quality while maintaining HIPAA compliance.
- Financial Services A fintech company integrates transaction data from multiple payment processors, customer data from their CRM, fraud detection systems, and regulatory reporting databases. This enables real-time fraud alerts and automated compliance reporting.
- SaaS Company A B2B software company integrates product usage data, customer support tickets, subscription billing, and sales pipeline information. Customer success teams get early warnings about churn risk and can proactively engage at-risk accounts.
- Ad-Tech Platform A video advertising platform like Performoo integrates data from multiple sources to optimize campaign performance. They combine ad impression data, video player analytics, advertiser campaign metrics, publisher inventory data, and real-time bidding information. This integration enables them to serve billions of ads monthly with AI-driven optimization, provide unified dashboards for advertisers and publishers, and deliver actionable insights on viewability, engagement, and conversion rates across all platforms.
Common Data Integration Tools & Platforms
The data integration landscape includes powerful enterprise solutions and modern cloud-native platforms:
Enterprise ETL Tools:
- Informatica PowerCenter – Industry-leading enterprise data integration with extensive connectivity
- IBM DataStage – Robust ETL platform for complex enterprise environments
- Talend – Open-source and enterprise data integration with strong community support
Cloud Data Integration Platforms:
- Microsoft Azure Data Factory – Native Azure integration with hybrid capabilities
- AWS Glue – Serverless ETL service for AWS ecosystems
- Google Cloud Dataflow – Stream and batch data processing on Google Cloud
Modern ELT and Reverse ETL:
- Fivetran – Automated data connectors for cloud data warehouses
- Airbyte – Open-source data integration with extensive connector library
- Stitch – Simple, scalable data pipeline platform
Data Warehouse Platforms with Built-In Integration:
- Snowflake – Cloud data warehouse with native data sharing capabilities
- Databricks – Unified analytics platform for data engineering and science
Each tool has strengths depending on your infrastructure, budget, technical expertise, and specific use cases.
Challenges in Data Integration
Despite its benefits, data integration comes with real challenges:
- Data Quality Issues: Source systems often contain incomplete, inconsistent, or duplicate data. Poor data quality leads to unreliable insights and wasted integration efforts.
- Complex Data Transformations: Mapping data from dozens of different schemas and formats requires significant technical expertise and ongoing maintenance.
- System Compatibility: Legacy systems may lack modern APIs or connectors, requiring custom development or middleware solutions.
- Performance and Scalability: As data volumes grow, integration processes can become slow and resource-intensive, impacting business operations.
- Security and Compliance: Integrating data across systems increases security risks and complicates compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2.
- Cost Management: Enterprise data integration tools can be expensive, and cloud data transfer costs add up quickly at scale.
- Change Management: Business requirements evolve, source systems update, and new data sources emerge—requiring constant maintenance of integration pipelines.
Benefits of Enterprise Data Integration
When done right, enterprise data integration delivers transformative benefits:
- Single Source of Truth: Eliminate conflicting reports and data discrepancies by creating one authoritative data source that everyone trusts.
- Faster Decision-Making: Real-time dashboards and automated reporting mean insights reach decision-makers when they matter most, not days or weeks later.
- Improved Customer Intelligence: Unified customer data from sales, marketing, support, and product usage creates comprehensive 360-degree customer views.
- Cost Reduction: Automation eliminates manual data entry and reduces the need for specialized reporting resources.
- Enhanced Innovation: When data scientists and analysts spend less time finding and preparing data, they spend more time discovering insights and building predictive models.
- Competitive Advantage: Organizations that can quickly integrate new data sources—from acquisitions, partnerships, or emerging technologies—adapt faster to market changes.
- Better Collaboration: When all departments work from the same integrated data, silos break down and cross-functional collaboration improves.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What’s the difference between data integration and data migration?
Ans: Data integration is an ongoing process of connecting and synchronizing data between systems, while data migration is a one-time project to move data from one system to another (like switching CRM platforms).
Q: Do I need a data warehouse for data integration?
Ans: Not necessarily. While data warehouses are common targets for integrated data, you can also integrate data into operational databases, data lakes, or even directly between applications using APIs.
Q: How much does data integration cost?
Ans: Costs vary dramatically based on data volume, number of sources, complexity, and chosen tools. Small businesses might spend a few hundred dollars monthly on cloud integration platforms, while enterprise implementations can cost hundreds of thousands annually.
Q: Can data integration work with legacy systems?
Ans: Yes, though it may require custom connectors or middleware. Many modern integration platforms offer pre-built connectors for common legacy databases and systems.
Q: What’s the difference between data integration and data orchestration?
Ans: Data integration focuses on combining data from different sources, while data orchestration manages the workflow and scheduling of data tasks across the entire data pipeline.
READ ALSO:- How AI Uses Harmonized Ad Data to Optimize Campaigns
Conclusion
Understanding what data integration is represents the first step toward building a truly data-driven organization. As businesses generate and collect more data than ever before, the ability to combine, transform, and deliver that data efficiently becomes a critical competitive differentiator.
Whether you’re implementing your first data integration project or optimizing an existing enterprise data integration strategy, the principles remain the same: identify your data sources, choose the right integration approach for your needs, invest in quality tools and processes, and continuously monitor and improve your data pipelines.
The organizations that master data integration don’t just have better reports—they make faster decisions, deliver superior customer experiences, and adapt more quickly to changing market conditions.
Ready to start your data integration journey? Begin by auditing your current data sources, identifying your most critical integration needs, and evaluating data integration platforms that align with your technical capabilities and business goals. The investment you make in proper data integration today will pay dividends for years to come.
Related Articles
Continue your learning journey with these related insights
What’s the Difference Between AdTech and MarTech?
In today’s digital-first world, marketing success depends heavily on technology. Two terms you’ll hear constantly are MarTech and AdTech. While they often work together, they serve very different purposes. Understanding the differences between martech and adtech is essential for building effective marketing strategies, enhancing customer experience, and maximizing return on investment (ROI). This guide explains […]

Everything You Need to Know About First-Party Data
In today’s privacy-first digital landscape, understanding first-party data has become crucial for businesses seeking to establish meaningful customer relationships while complying with evolving regulations. First-party data is information that companies collect directly from their customers through their own channels, making it the most valuable and reliable data source available to modern marketers. As third-party cookies […]
Ready to Transform Your Advertising Strategy?
Join thousands of advertisers who trust Performoo to optimize their campaigns and maximize revenue.